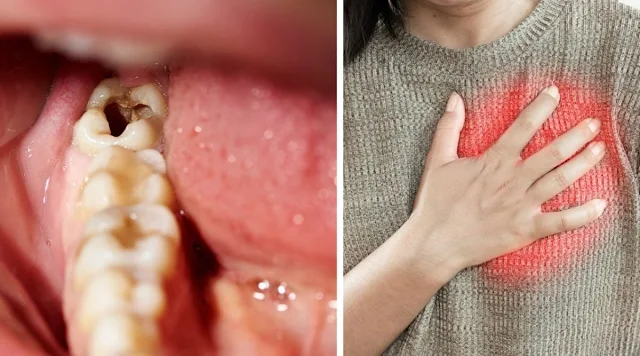
You might think that cavities are a mild condition. But untreated tooth decay causes heart disease and attacks other organs. Going to the dentist is never a pleasure. And for good reason, fear of the dentist is very common since it concerns more than half of the French population. But when our teeth are damaged to the point of causing pain, this consultation is necessary. In addition, cavities are a common disease that can affect any age. Often seen as benign, it can progress and cause serious heart problems and attack other organs.
From a very young age, our parents instilled in us the need for good oral hygiene. The principles of prevention involving regular brushing of teeth and moderate consumption of sweets had all their legitimacy. In reality, certain factors can damage tooth tissue and cause serious health problems.
What is a cavity?
Caries is the most common dental condition. It is an infectious disease that causes progressive destruction of tooth tissue. Some bacteria can build up inside dental plaque and damage teeth. First, decay attacks the enamel which undergoes demineralization. Then bacteria can damage dentin and make teeth sensitive and painful.
What are the causes of the disease?
According to Keyes' scheme, certain factors are likely to cause cavities.
- Bacterial dental plaque:
It is estimated that the mouth contains more than 60 species of bacteria that form bacterial plaque. Among them are anaerobic germs that can cause gum disease. In addition, streptococci and lactobacilli are the bacteria involved in the development of cavities. So the more a person gets these microbes in their mouth, the more likely they are to have dental cavities.
- Food:
It's no secret that food choices play an important role in the formation of cavities. Foods that contain acids can demineralize enamel. Finally, foods high in sugar promote the formation of dental plaque.
- Field :
It is clear that we are not all equal in the face of dental pathologies. Some people have more fragile teeth, for example with a thinner, poorly mineralized enamel. Thus, bacteria will be more able to destroy the teeth of these people.
- Time: a cavity gradually forms when the three previous factors are combined. Therefore, time is an important component to take into account.
What are the stages of evolution of a cavity?
Untreated cavities can progress to more advanced stages.
Stage 1: Demineralization of the enamel
When caries is in its first stage, it causes demineralization of the enamel. Generally, the onset of the disease goes unnoticed as there is no pain. Nevertheless, regular check-ups with the doctor can detect the demineralization of the enamel and slow down the development of the disease.
Stage 2: Damage to the dentin
After destroying the enamel, cavities can attack the dentin. Thus, sensitization can be observed in the decayed tooth. At this point, cavities do appear as a brown spot or a hole in the tooth. Generally, the dentist removes the infected tissue and places a dental amalgam.
Stage 3: Inflammation of the pulp
If caries is not treated in its second stage, it will progress to inflammation of the pulp. The latter represents a deeper layer of the tooth. Thus, the person may experience what is commonly called a "toothache". A visit to the dentist will be essential to curb the development of bacteria and avoid tooth abscess.
Stage 4: Dental abscess
This last stage is marked by the development of the infection and the accumulation of pus. Unfortunately, the doctor has no choice but to extract the infected tooth.
What are the potential complications ?
Contrary to what most people think, cavities are not always a mild condition. If left untreated at an early stage, it can progress to affect many organs. As the Cardio-Vascular Research Foundation of the Institut de France explains, the accumulation of bacteria